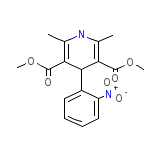
Nifar




Nifar Brand names, Nifar Analogs
- Adalat
- Adalat 10
- Adalat 20
- Adalat 5
- Adalat CC
- Adalat CR
- Adalat Crono
- Adalat Ft
- Adalat Gits
- Adalat Gits 30
- Adalat LA
- Adalat LP
- Adalat Oros
- Adalat PA
- Adalat Retard
- Adalate
- Adapine
- Adapress
- Alat
- Aldipin
- Alfadal
- Alonix
- Alonix S
- Alpha-Nifedipine Retard
- Angipec
- Anifed
- Anpine
- Apo-Nifed
- Aprical
- Bonacid
- Calcibloc
- Calcigard
- Calcilat
- Camont
- Cardifen
- Cardilat
- Cardilate
- Cardionorm
- Chronadalate
- Chronadalate Lp
- Citilat
- Coracten
- Coral
- Cordafen
- Cordaflex
- Cordalat
- Cordicant
- Cordilan
- Cordipin
- Corinfar
- Corotrend
- Corynphar
- Depin
- Dignokonstant
- Dilafed
- Dilcor
- Dipinkor
- Duranifin
- Ecodipi
- Ecodipin
- Ecodipin E
- Fedcor
- Fedcor Retard
- Fenamon
- Fenamon Sr
- Fenihidin
- Fenihidine
- Glopir
- Hadipin
- Hexadilat
- Introcar
- Kordafen
- Macorel
- Megalat
- Myogard
- N1fedilat
- Nedipin
- Nicardia
- Nifangin
- Nifar
- Nifdemin
- Nifebene
- Nifecard
- Nifecor
- Nifedepat
- Nifedicor
- Nifedin
- Nifedine
- Nifedipine Retard
- Nifedipres
- Nifedirex LP
- Nifelan
- Nifelat
- Nifelat Q
- Nifelate
- Nifensar XL
- Nificard
- Nifidine
- Nifipen
- Niphedipine
- Orix
- Oxcord
- Pidilat
- Procardia
- Procardia XL
- Sepamit
- Tibricol
- Zenusin
Nifar Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
Nifar Chemical_Formula
C17H18N2O6
Nifar RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic2/nifedip.htm
Nifar fda sheet
Nifar msds (material safety sheet)
Nifar Synthesis Reference
Bossert, Vater, U.S. Pat. 3,485,847 (1969)
Nifar Molecular Weight
346.335 g/mol
Nifar Melting Point
172 - 174 oC
Nifar H2O Solubility
Insoluble
Nifar State
Solid
Nifar LogP
2.343
Nifar Dosage Forms
Capsule; Tablet; Tablet (extended-release)
Nifar Indication
For the management of vasospastic angina, chronic stable angina and hypertension.
Nifar Pharmacology
Nifedipine, the prototype of the dihydropyridine class of calcium-channel antagonists, is similar to other dihydropyridines including amlodipine, felodipine, isradipine, and nicardipine. Nifedipine is used to treat Prinzmetal's angina, hypertension, and other vascular disorders such as Raynaud's phenomenon. By blocking the calcium channels, Nifedipine inhibits the spasm of the coronary artery and dilates the systemic arteries, results in a increase of myocardial oxygen supply and a decrease in systemic blood pressure.
Nifar Absorption
Rapidly and fully absorbed following oral administration.
Nifar side effects and Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, severe drop in blood pressure, slurred speech, and weakness. LD50=494 mg/kg (orally in mice); LD50=1022 mg/kg (orally in rats)
Nifar Patient Information
Nifar Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals