Aparasin




Aparasin Brand names, Aparasin Analogs
- Aalindan
- Aficide
- Agrocide
- Agrocide III
- Agrocide WP
- Ameisenmittel merck
- Ameisentod
- Aparasin
- Aphtiria
- Aplidal
- Arbitex
- Atlas steward
- BBH
- BHC
- Ben-Hex
- Bentox 10
- Benzene hexachloride
- Bexol
- Celanex
- Chloresene
- Codechine
- DBH
- Detmol-Extrakt
- Devoran
- Dol Granule
- Drilltox-Spezial Aglukon
- Entomoxan
- Esoderm
- Fumite lindane
- Gamacid
- Gamene
- Gamma-BHC dust
- Gamma-Col
- Gamma-HCH dust
- Gammalin
- Gammalin 20
- Gammasan
- Gammaterr
- Gammexane
- Gexane
- HCCH
- HCH
- HGI
- Heclotox
- Hexa
- Hexachloran
- Hexachlorane
- Hexachlorocyclohexane
- Hexatox
- Hexaverm
- Hexicide
- Hexit
- Hexyclan
- Hortex
- Indane
- Isotox
- Jacutin
- Kokotine
- Kwell
- Lendine
- Lentox
- Lidenal
- Lindafor
- Lindatox
- Lindex
- Lindosep
- Lintox
- Linvur
- Lorexane
- Milbol 49
- Mszycol
- Murfume grain store smoke
- Neo-Scabicidol
- New kotol
- Nexen FB
- Nexit
- Nexit-Stark
- Nexol-E
- Nicochloran
- Omnitox
- Ovadziak
- Owadziak
- PMS Lindane
- Pedraczak
- Pflanzol
- Quellada
- Sang-«gamma»
- Scabene
- Scabene lotion
- Spritz-Rapidin
- Spruehpflanzol
- Streunex
- TAP 85
- Thionex
- Tri-6
- Viton
- beta-BHC
- beta-Hexachlorocyclohexane
- beta-Lindane
Aparasin Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
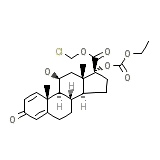
Aparasin Chemical_Formula
C24H31ClO7
Aparasin RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic2/lotemax.htm
Aparasin fda sheet
Aparasin msds (material safety sheet)
Aparasin Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
Aparasin Molecular Weight
466.951 g/mol
Aparasin Melting Point
220-224 oC
Aparasin H2O Solubility
5 mg/mL
Aparasin State
Solid
Aparasin LogP
4.004
Aparasin Dosage Forms
Solution; Spray
Aparasin Indication
As an ophthalmic it is used for the treatment of steroid responsive inflammatory conditions of the eye such as allergic conjunctivitis, uveitis, acne rosacea, superficial punctate keratitis, herpes zoster keratitis, iritis, cyclitis, and selected infective conjunctivitides. As a nasal spray, used for the treatment and management of seasonal allergic rhinitis.
Aparasin Pharmacology
Loteprednol etabonate (LE) is a "soft" steroid belonging to a unique class of glucocorticoids. LE possesses a metabolically labile 17 beta-chloromethyl ester function which was designed in order to be hydrolyzed to an inactive carboxylic acid moiety. This inactive metabolite is more hydrophilic and is thus readily eliminated from the body. Loteprednol etabonate has good ocular permeation properties and good skin permeation properties similar to "hard" steroids. It is used as a topical agent for the treatment of steroid responsive inflammatory conditions of the eye such as allergic conjunctivitis, uveitis and iritis.
Aparasin Absorption
Very limited systemic absorption, but good absorption at the point of delivery.
Aparasin side effects and Toxicity
Adverse effects include abnormal vision / blurring, burning on instillation, chemosis, discharge, dry eyes, epiphora, foreign body sensation, itching, injection, and photophobia.
Aparasin Patient Information
Aparasin Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals