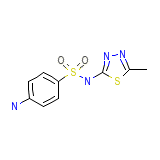
Sulphamethyltiadiazole




Sulphamethyltiadiazole Brand names, Sulphamethyltiadiazole Analogs
- Ayerlucil
- Famet
- Lucosil
- Methazol
- Microsul
- Proklar
- Renasul
- Rufol
- SULFAMETHIAZOLE
- Salimol
- Solfametizolo [Dcit]
- Sulamethizole
- Sulfa Gram
- Sulfamethazole
- Sulfamethizol
- Sulfamethizole [Usan:Inn:Jan]
- Sulfamethizolum [Inn-Latin]
- Sulfamethylthiadiazole
- Sulfametizol [Inn-Spanish]
- Sulfapyelon
- Sulfstat
- Sulfurine
- Sulphamethizole
- Sulphamethyltiadiazole
- Tetracid
- Thidicur
- Thiosulfil
- Thiosulfil Forte
- Ultrasul
- Urocydal
- Urodiaton
- Urolucosil
- Urosulfin
- Uroz
Sulphamethyltiadiazole Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
Sulphamethyltiadiazole Chemical_Formula
C9H10N4O2S2
Sulphamethyltiadiazole RX_link
No information avaliable
Sulphamethyltiadiazole fda sheet
Sulphamethyltiadiazole msds (material safety sheet)
Sulphamethyltiadiazole Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
Sulphamethyltiadiazole Molecular Weight
270.333 g/mol
Sulphamethyltiadiazole Melting Point
208 oC
Sulphamethyltiadiazole H2O Solubility
1050 mg/L
Sulphamethyltiadiazole State
Solid
Sulphamethyltiadiazole LogP
2.968
Sulphamethyltiadiazole Dosage Forms
Tablet
Sulphamethyltiadiazole Indication
For the treatment of urinary tract infection
Sulphamethyltiadiazole Pharmacology
Sulfamethizole is a sulfonamide antibiotic. The sulfonamides are synthetic bacteriostatic antibiotics with a wide spectrum against most gram-positive and many gram-negative organisms. However, many strains of an individual species may be resistant. Sulfonamides inhibit multiplication of bacteria by acting as competitive inhibitors of p-aminobenzoic acid in the folic acid metabolism cycle. Bacterial sensitivity is the same for the various sulfonamides, and resistance to one sulfonamide indicates resistance to all. Most sulfonamides are readily absorbed orally. However, parenteral administration is difficult, since the soluble sulfonamide salts are highly alkaline and irritating to the tissues. The sulfonamides are widely distributed throughout all tissues. High levels are achieved in pleural, peritoneal, synovial, and ocular fluids. Although these drugs are no longer used to treat meningitis, CSF levels are high in meningeal infections. Their antibacterial action is inhibited by pus.
Sulphamethyltiadiazole Absorption
Rapidly absorbed.
Sulphamethyltiadiazole side effects and Toxicity
No information avaliable
Sulphamethyltiadiazole Patient Information
Sulphamethyltiadiazole Organisms Affected
Enteric bacteria and other eubacteria