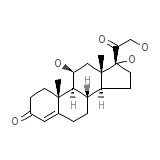
EF corlin




EF corlin Brand names, EF corlin Analogs
- 11beta-Hydroxycortisone
- 17alpha-Hydroxycorticosterone
- A-hydrocort
- Acticort
- Aeroseb HC
- Aeroseb-HC
- Ala-Scalp
- Ala-cort
- Alacort
- Algicirtis
- Alphaderm
- Amberin
- Anflam
- Anti-inflammatory hormone
- Anusol HC
- Aquacort
- Aquanil HC
- Balneol-hc
- Barseb HC
- Basan-Corti
- Beta-hc
- CaldeCORT Spray
- Cetacort
- Clear aid
- Cleiton
- Cobadex
- Colocort
- Cortaid
- Compound F
- Cort-Dome
- Cort-Quin
- Cortanal
- Cortef
- Cortef Acetate
- Cortenema
- Cortesal
- Corticreme
- Cortifan
- Cortifoam
- Cortiment
- Cortisol
- Cortisol alcohol
- Cortisolonum
- Cortisone, tetrahydro-
- Cortisporin
- Cortisporin Otico
- Cortispray
- Cortolotion
- Cortonema
- Cortoxide
- Cortril
- Cremesone
- Cremicort-H
- Cutisol
- Delacort
- Derm-Aid
- Dermacort
- Dermaspray
- Dermil
- Dermocortal
- Dermolate
- Dihydrocostisone
- Dioderm
- Dome-cort
- Domolene-HC
- Dricort
- Drotic
- EF corlin
- Efcorbin
- Efcortelan
- Efcortelin
- Eldecort
- Eldercort
- Epicort
- Epiderm H
- Esiderm H
- Evacort
- Ficortril
- Fiocortril
- Flexicort
- Foille Insetti
- Genacort
- Glycort
- Gyno-Cortisone
- H-Cort
- Heb Cort
- Heb-Cort
- Hemsol-HC
- Hi-cor
- Hidalone
- Hidro-Colisona
- Hidrocortisona [INN-Spanish]
- Hycort
- Hycortol
- Hycortole
- Hydracort
- Hydrasson
- Hydro-adreson
- Hydro-colisona
- Hydrocort
- Hydrocortal
- Hydrocorticosterone
- Hydrocortisone Acetate
- Hydrocortisone Base
- Hydrocortisone Butyrate
- Hydrocortisone Sodium Phosphate
- Hydrocortisone Sodium Succinate
- Hydrocortisone Valerate
- Hydrocortisone [BAN:INN:JAN]
- Hydrocortisone alcohol
- Hydrocortisone free alcohol
- Hydrocortisonum [INN-Latin]
- Hydrocortistab
- Hydrocortisyl
- Hydrocortone
- Hydroskin
- Hydroxycortisone
- Hysone
- Hytisone
- Hytone
- Hytone lotion
- Idrocortisone [DCIT]
- Incortin-H
- Incortin-hydrogen
- Kendall's compound F
- Komed HC
- Kyypakkaus
- Lacticare HC
- Lacticare-HC
- Lactisona
- Locoid
- Locoid Lipocream
- Lubricort
- Maintasone
- Medicort
- Meusicort
- Micort-hc
- Mildison
- Milliderm
- Neosporin-H Ear
- Nogenic HC
- Nutracort
- Nystaform-HC
- Optef
- Orabase HCA
- Otalgine
- Otobiotic
- Otocort
- Otosone-F
- Pandel
- Pediotic Suspension
- Penecort
- Permicort
- Polcort H
- Preparation H Hydrocortisone Cream
- Prepcort
- Prevex HC
- Proctocort
- Proctofoam
- Protocort
- Racet
- Rectoid
- Reichstein's Substance M
- Remederm HC
- Sanatison
- Scalpicin Capilar
- Schericur
- Scheroson F
- Sigmacort
- Signef
- Solu-cortef
- Stie-cort
- Stiefcorcil
- Synacort
- Systral Hydrocort
- THE
- Tarcortin
- Tetrahydro E
- Tetrahydrocompound E
- Texacort
- Texacort lotion 25
- Thyrotropic-releasing factor
- Timocort
- Topicort
- Transderma H
- Traumaide
- Uniderm
- Urocortisone
- Vioform-Hydrocortisone
- VoSol HC
- Vytone
- Westcort
- Zenoxone
EF corlin Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
EF corlin Chemical_Formula
C21H30O5
EF corlin RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic/hydrocortisone.htm
EF corlin fda sheet
EF corlin msds (material safety sheet)
EF corlin Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
EF corlin Molecular Weight
362.46 g/mol
EF corlin Melting Point
220 oC
EF corlin H2O Solubility
320 mg/L
EF corlin State
Solid
EF corlin LogP
1.692
EF corlin Dosage Forms
Cream; Ointment; Enemas
EF corlin Indication
For the relief of the inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses. Also used to treat endocrine (hormonal) disorders (adrenal insufficiency, Addisons disease). It is also used to treat many immune and allergic disorders, such as arthritis, lupus, severe psoriasis, severe asthma, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn's disease.
EF corlin Pharmacology
Hydrocortisone is the most important human glucocorticoid. It is essential for life and regulates or supports a variety of important cardiovascular, metabolic, immunologic and homeostatic functions. Topical hydrocortisone is used for its anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive properties to treat inflammation due to corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses. Glucocorticoids are a class of steroid hormones characterised by an ability to bind with the cortisol receptor and trigger a variety of important cardiovascular, metabolic, immunologic and homeostatic effects. Glucocorticoids are distinguished from mineralocorticoids and sex steroids by having different receptors, target cells, and effects. Technically, the term corticosteroid refers to both glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, but is often used as a synonym for glucocorticoid. Glucocorticoids suppress cell-mediated immunity. They act by inhibiting genes that code for the cytokines IL-1, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-alpha, the most important of which is the IL-2. Reduced cytokine production limits T cell proliferation. Glucocorticoids also suppress humoral immunity, causing B cells to express lower amounts of IL-2 and IL-2 receptors. This diminishes both B cell clonal expansion and antibody synthesis. The diminished amounts of IL-2 also leads to fewer T lymphocyte cells being activated.
EF corlin Absorption
Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from normal intact skin. Inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin increase percutaneous absorption.
EF corlin side effects and Toxicity
Side effects include inhibition of bone formation, suppression of calcium absorption and delayed wound healing
EF corlin Patient Information
No information avaliable
EF corlin Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals