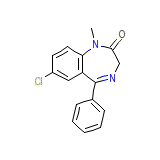
Aliseum




Aliseum Brand names, Aliseum Analogs
- Alboral
- Aliseum
- Alupram
- Amiprol
- An-Ding
- Ansiolin
- Ansiolisina
- Apaurin
- Apo-Diazepam
- Apozepam
- Armonil
- Assival
- Atensine
- Atilen
- Bensedin
- Bialzepam
- Calmocitene
- Calmpose
- Cercine
- Ceregulart
- Condition
- DAP
- Diacepan
- Dialag
- Dialar
- Diapam
- Diastat
- Diazemuls
- Diazemulus
- Diazepam Intensol
- Diazepan
- Diazetard
- Dienpax
- Dipam
- Dipezona
- Dizac
- Domalium
- Duksen
- Duxen
- E-Pam
- Eridan
- Eurosan
- Evacalm
- Faustan
- Faustan,
- Freudal
- Frustan
- Gewacalm
- Gihitan
- Horizon
- Kabivitrum
- Kiatrium
- LA III
- La-Iii
- Lamra
- Lembrol
- Levium
- Liberetas
- Mandrozep
- Methyldiazepinone
- Methyldiazepinone, Pharmaceutical
- Morosan
- Neurolytril
- Noan
- Novazam
- Novo-Dipam
- Paceum
- Pacitran
- Paranten
- Paxate
- Paxel
- Plidan
- Pms-Diazepam
- Pro-Pam
- Q-Pam
- Q-Pam Relanium
- Quetinil
- Quiatril
- Quievita
- Relaminal
- Relanium
- Relax
- Renborin
- Ruhsitus
- S.A. R.L.
- Saromet
- Sedapam
- Sedipam
- Seduksen
- Seduxen
- Serenack
- Serenamin
- Serenzin
- Servizepam
- Setonil
- Sibazon
- Sibazone
- Solis
- Sonacon
- Stesolid
- Stesolin
- Tensopam
- Tranimul
- Tranqdyn
- Tranquase
- Tranquirit
- Tranquo-Puren
- Tranquo-Tablinen
- Umbrium
- Unisedil
- Usempax Ap
- Valaxona
- Valeo
- Valiquid
- Valitran
- Valium
- Valrelease
- Vatran
- Velium
- Vival
- Vivol
- Zetran
- Zipan
Aliseum Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
Aliseum Chemical_Formula
C16H13ClN2O
Aliseum RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic/diazepam.htm
Aliseum fda sheet
Aliseum msds (material safety sheet)
Aliseum Synthesis Reference
Reeder, Sternbach; U.S. Pat. 3,371,085 (1968)
Aliseum Molecular Weight
284.74 g/mol
Aliseum Melting Point
125-126oC
Aliseum H2O Solubility
Slightly soluble (50 mg/L)
Aliseum State
solid
Aliseum LogP
2.988
Aliseum Dosage Forms
Tablets; Injectable solution
Aliseum Indication
Used in the treatment of severe anxiety disorders, as a hypnotic in the short-term management of insomnia, as a sedative and premedicant, as an anticonvulsant, and in the management of alcohol withdrawal syndrome.
Aliseum Pharmacology
Diazepam, a benzodiazepine, generates the same active metabolite as chlordiazepoxide and clorazepate. In animals, diazepam appears to act on parts of the limbic system, the thalamus and hypothalamus, and induces calming effects. Diazepam, unlike chlorpromazine and reserpine, has no demonstrable peripheral autonomic blocking action, nor does it produce extrapyramidal side effects; however, animals treated with diazepam do have a transient ataxia at higher doses. Diazepam was found to have transient cardiovascular depressor effects in dogs. Long-term experiments in rats revealed no disturbances of endocrine function. Injections into animals have produced localized irritation of tissue surrounding injection sites and some thickening of veins after intravenous use.
Aliseum Absorption
Essentially complete, with a bioavailability of 93%.
Aliseum side effects and Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include somnolence, confusion, coma, and diminished reflexes. Respiration, pulse and blood pressure should be monitored.
Aliseum Patient Information
Aliseum Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals