KAN




KAN Brand names, KAN Analogs
KAN Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
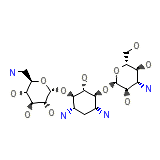
KAN Chemical_Formula
C18H36N4O11
KAN RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic3/kanamycin.htm
KAN fda sheet
KAN msds (material safety sheet)
KAN Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
KAN Molecular Weight
484.499 g/mol
KAN Melting Point
No information avaliable
KAN H2O Solubility
No information avaliable
KAN State
Solid
KAN LogP
-7.936
KAN Dosage Forms
No information avaliable
KAN Indication
For treatment of infections where one or more of the following are the known or suspected pathogens: E. coli, Proteus species (both indole-positive and indole-negative), E. aerogenes, K. pneumoniae, S. marcescens, and Acinetobacter species.
KAN Pharmacology
Kanamycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic. Aminoglycosides work by binding to the bacterial 30S ribosomal subunit, causing misreading of t-RNA, leaving the bacterium unable to synthesize proteins vital to its growth. Aminoglycosides are useful primarily in infections involving aerobic, Gram-negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, and Enterobacter. In addition, some mycobacteria, including the bacteria that cause tuberculosis, are susceptible to aminoglycosides. Infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria can also be treated with aminoglycosides, but other types of antibiotics are more potent and less damaging to the host. In the past the aminoglycosides have been used in conjunction with penicillin-related antibiotics in streptococcal infections for their synergistic effects, particularly in endocarditis. Aminoglycosides are mostly ineffective against anaerobic bacteria, fungi and viruses.
KAN Absorption
No information avaliable
KAN side effects and Toxicity
LD 50 - ORAL, MOUSE = 17500 MG/KG, LD 50 - ORAL, RAT = >4 GM/KG, LD 50 - ORAL, RABBIT = >3 GM/KG
KAN Patient Information
No information avaliable
KAN Organisms Affected
Enteric bacteria and other eubacteria