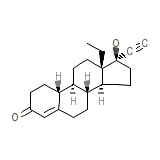
Ovrette




Categorie
Ovrette Les marques, Ovrette Analogs
- Alesse
- Alpha-Norgestrel
- Component of Lo/Ovral
- Component of Ovral
- D-Norgestrel
- DL-Norgestrel
- Follistrel
- Jadelle
- LD Norgestrel
- Ld Norgestrel [French]
- Levlen
- Levlen Ed
- Levonorgestrel
- Levonorgestrel Implants
- Levonorgestrel [Usan:Ban:Inn]
- Levonorgestrelum [Inn-Latin]
- Levonova
- Levora-21
- Levora-28
- Lo/Ovral
- Logynon
- Logynon Ed
- Methylnorethindrone
- Microgest Ed
- Microgyn
- Microgynon
- Microgynon 21
- Microgynon 28
- Microgynon 30 Ed
- Microgynon Cd
- Microlut
- Microlution
- Microval
- Minivlar 30
- Mirena
- Monofeme 28
- Monovar
- NOG
- Neogest
- Neogynon 21
- Nordet
- Nordette
- Nordette 21
- Nordette 28
- Norgeston
- Norgestrel [Progestins]
- Norgestrel [Usan:Ban:Inn:Jan]
- Norgestrelum [Inn-Latin]
- Norplant
- Norplant 2
- Norplant II
- Norplant System in Plastic Container
- Ovral
- Ovral-Lo
- Ovran
- Ovranette
- Ovrette
- Plan B
- Postinor
- Preven
- Rigevidon 21+7
- Stediril
- Stediril 30
- Tetragynon
- Tri-Levlen
- Tri-Levlen 21
- Triagynon
- Triciclor
- Trifeme 28
- Trigoa
- Trinordiol
- Trinordiol 21
- Trinordiol 28
- Triphasil
- Triphasil 21
- Triphasil 28
- Triquilar Ed
- Trivora
Ovrette Les marques melange
Ovrette Formule chimique
C21H28O2
Ovrette RX lien
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic/norgeth.htm
Ovrette FDA fiche
Ovrette msds (fiche de securite des materiaux)
Ovrette Synthese de reference
GA Smith, H. Smith, le brevet américain. 3,959,322 (1976)
Ovrette Poids moleculaire
312.446 g/mol
Ovrette Point de fusion
206oC
Ovrette H2O Solubilite
Aucune information disponible
Ovrette Etat
Solid
Ovrette LogP
3.251
Ovrette Formes pharmaceutiques
Tablet
Ovrette Indication
Utilisé comme un contraceptif oral pour empêcher la grossesse
Ovrette Pharmacologie
Norgestrel est utilisé comme un contraceptif féminin. Le norgestrel est un progestatif ou une forme synthétique de l'hormone naturelle du sexe féminin, la progestérone. En temps normal, une femme cycle menstruel, un ovule mûrit et est libéré par les ovaires (l'ovulation). L'ovaire produit alors la progestérone, empêchant la libération des ovules plus loin et l'amorçage de la muqueuse de l'utérus pour une éventuelle grossesse. Si une grossesse survient, taux de progestérone dans le corps restent élevés, le maintien de la muqueuse utérine. Si la grossesse ne se produit pas, les niveaux de progestérone dans la chute du corps, résultant en une période menstruelle. Astuces Norgestrel le corps processus en pensant que l'ovulation a déjà eu lieu, en maintenant des niveaux élevés de la progestérone de synthèse. Ceci empêche la libération d'ovules par les ovaires.
Ovrette Absorption
65%
Ovrette Toxicite
Nausées, vomissements, somnolence et / fatigue, des saignements de retrait; DL50 = mg / kg (par voie orale chez le rat)
Ovrette Information pour les patients
PATIENT INFORMATION
WHEN TO START THE FIRST PACK OF PILLS
For the 21-day pill pack you have two choices of which day to start taking your first pack of
pills. (See DAY 1 START or SUNDAY START directions below.) Decide with your health-care
professional which is the best day for you. The 28-day pill pack accommodates a SUNDAY START only.
For either pill pack pick a time of day which will be easy to remember.
DAY 1 START
These instructions are for the 21-day pill pack only. The 28-day pill pack does not accommodate a
DAY 1 START dosage regimen.
1. Take the first "active" white pill of the first pack during the first 24 hours of your period.
2. You will not need to use a back-up nonhormonal method of birth control, since you are starting
the pill at the beginning of your period.
SUNDAY START
These instructions are for either the 21-day or the 28-day pill pack.
1. Take the first "active" white pill of the first pack on the Sunday after your period starts, even
if you are still bleeding. If your period begins on Sunday, start the pack that same day.
2. Use a nonhormonal method of birth control (such as condoms and/or spermicide) as a backup method if
you have sex anytime from the Sunday you start your first pack until the next Sunday (7 days).
WHAT TO DO DURING THE MONTH
1. TAKE ONE PILL AT THE SAME TIME EVERY DAY UNTIL THE PACK IS EMPTY.
Do not skip pills even if you are spotting or bleeding between monthly periods or feel sick to your
stomach (nausea).
Do not skip pills even if you do not have sex very often.
2. WHEN YOU FINISH A PACK OR SWITCH YOUR BRAND OF PILLS:
21 pills: Wait 7 days to start the next pack. You will probably have your period during that week. Be
sure that no more than 7 days pass between 21-day packs.
28 pills: Start the next pack on the day after your last "reminder" pill. Do not wait any days between
packs.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU MISS PILLS
The pill may not be as effective if you miss white "active" pills, and particularly if you miss the first
few or the last few white "active" pills in a pack.
If you MISS 1 white "active" pill:
1. Take it as soon as you remember. Take the next pill at your regular time. This means you may take 2 pills
in 1 day.
2. You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you miss pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal
birth-control method (such as condoms and/or spermicide) as a backup for those 7 days.
If you MISS 2 white "active" pills in a row in WEEK 1 OR WEEK 2 of your pack:
1. Take 2 pills on the day you remember and 2 pills the next day.
2. Then take 1 pill a day until you finish the pack.
3. You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you miss pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal
birth-control method (such as condoms and/or spermicide) as a backup for those 7 days.
If you MISS 2 white "active" pills in a row in THE 3rd WEEK:
The Day 1 Starter instructions are for the 21-day pill pack only. The 28-day pill pack does not accommodate a
DAY 1 START dosage regimen. The Sunday Starter instructions are for either the 21-day or 28-day pill pack.
1. If you are a Day 1 Starter:
THROW OUT the rest of the pill pack and start a new pack that same day.
If you are a Sunday Starter:
Keep taking 1 pill every day until Sunday.
On Sunday, THROW OUT the rest of the pack and start a new pack of pills that same day.
2. You may not have your period this month but this is expected. However, if you miss your period 2 months in a
row, call your health-care professional because you might be pregnant.
3. You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you miss pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal
birth-control method (such as condoms and/or spermicide) as a backup for those 7 days.
If you MISS 3 OR MORE white "active" pills in a row (during the first 3 weeks):
The Day 1 Starter instructions are for the 21-day pill pack only. The 28-day pill pack does not accommodate a
DAY 1 START dosage regimen. The Sunday Starter instructions are for either the 21-day or 28-day pill pack.
1. If you are a Day 1 Starter:
THROW OUT the rest of the pill pack and start a new pack that same day.
If you are a Sunday Starter:
Keep taking 1 pill every day until Sunday.
On Sunday, THROW OUT the rest of the pack and start a new pack of pills that same day.
2. You may not have your period this month but this is expected. However, if you miss your period 2 months in a
row, call your health-care professional because you might be pregnant.
3. You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you miss pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal
birth-control method (such as condoms and/or spermicide) as a backup for those 7 days.
A REMINDER FOR THOSE ON 28-DAY PACKS
If you forget any of the 7 pink "reminder" pills in Week 4:
THROW AWAY the pills you missed.
Keep taking 1 pill each day until the pack is empty.
You do not need a back-up nonhormonal birth-control method if you start your next pack on time.
FINALLY, IF YOU ARE STILL NOT SURE WHAT TO DO ABOUT THE PILLS YOU HAVE MISSED
Use a BACK-UP NONHORMONAL BIRTH-CONTROL METHOD anytime you have sex.
KEEP TAKING ONE PILL EACH DAY until you can reach your health-care professional.
PREGNANCY DUE TO PILL FAILURE
The incidence of pill failure resulting in pregnancy is approximately 1% if taken every day as directed, but the
average failure rate is approximately 5% including women who do not always take the pill exactly as directed
without missing any pills. If you do become pregnant, the risk to the fetus is minimal, but you should stop
taking your pills and discuss the pregnancy with your health-care professional.
PREGNANCY AFTER STOPPING THE PILL
There may be some delay in becoming pregnant after you stop using oral contraceptives, especially if you had
irregular menstrual cycles before you used oral contraceptives. It may be advisable to postpone conception until
you begin menstruating regularly once you have stopped taking the pill and desire pregnancy.
There does not appear to be any increase in birth defects in newborn babies when pregnancy occurs soon after
stopping the pill.
If you do not desire pregnancy, you should use another method of birth control immediately after stopping the
oral contraceptive pill.
OVERDOSE
Overdosage may cause nausea, vomiting, and fatigue/drowsiness. Withdrawal bleeding may occur in females. In
case of overdosage, contact your health-care professional or pharmacist.
OTHER INFORMATION
Your health-care professional will take a medical and family history before prescribing oral contraceptives
and will examine you. The physical examination may be delayed to another time if you request it and the health-
care professional believes that it is appropriate to postpone it. You should be reexamined at least once a year.
Be sure to inform your health-care professional if there is a family history of any of the conditions listed
previously in this leaflet. Be sure to keep all appointments with your health-care professional, because this
is a time to determine if there are early signs of side effects of oral-contraceptive use.
Do not use the drug for any condition other than the one for which it was prescribed. This drug has been
prescribed specifically for you; do not give it to others who may want birth-control pills.
HEALTH BENEFITS FROM ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
In addition to preventing pregnancy, use of oral contraceptives may provide certain benefits. They are:
� Menstrual cycles may become more regular.
� Blood flow during menstruation may be lighter, and less iron may be lost. Therefore, anemia due to iron
deficiency is less likely to occur.
� Pain or other symptoms during menstruation may be encountered less frequently.
� Ovarian cysts may occur less frequently.
� Ectopic (tubal) pregnancy may occur less frequently.
� Noncancerous cysts or lumps in the breast may occur less frequently.
� Acute pelvic inflammatory disease may occur less frequently.
� Oral-contraceptive use may provide some protection against developing two forms of cancer: cancer of the
ovaries and cancer of the lining of the uterus.
If you want more information about birth-control pills, ask your health-care professional or pharmacist. They
have a more technical leaflet called the Professional Labeling which you may wish to read.
WHEN TO START THE FIRST PACK OF PILLS
For the 21-day pill pack you have two choices of which day to start taking your first pack of
pills. (See DAY 1 START or SUNDAY START directions below.) Decide with your health-care
professional which is the best day for you. The 28-day pill pack accommodates a SUNDAY START only.
For either pill pack pick a time of day which will be easy to remember.
DAY 1 START
These instructions are for the 21-day pill pack only. The 28-day pill pack does not accommodate a
DAY 1 START dosage regimen.
1. Take the first "active" white pill of the first pack during the first 24 hours of your period.
2. You will not need to use a back-up nonhormonal method of birth control, since you are starting
the pill at the beginning of your period.
SUNDAY START
These instructions are for either the 21-day or the 28-day pill pack.
1. Take the first "active" white pill of the first pack on the Sunday after your period starts, even
if you are still bleeding. If your period begins on Sunday, start the pack that same day.
2. Use a nonhormonal method of birth control (such as condoms and/or spermicide) as a backup method if
you have sex anytime from the Sunday you start your first pack until the next Sunday (7 days).
WHAT TO DO DURING THE MONTH
1. TAKE ONE PILL AT THE SAME TIME EVERY DAY UNTIL THE PACK IS EMPTY.
Do not skip pills even if you are spotting or bleeding between monthly periods or feel sick to your
stomach (nausea).
Do not skip pills even if you do not have sex very often.
2. WHEN YOU FINISH A PACK OR SWITCH YOUR BRAND OF PILLS:
21 pills: Wait 7 days to start the next pack. You will probably have your period during that week. Be
sure that no more than 7 days pass between 21-day packs.
28 pills: Start the next pack on the day after your last "reminder" pill. Do not wait any days between
packs.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU MISS PILLS
The pill may not be as effective if you miss white "active" pills, and particularly if you miss the first
few or the last few white "active" pills in a pack.
If you MISS 1 white "active" pill:
1. Take it as soon as you remember. Take the next pill at your regular time. This means you may take 2 pills
in 1 day.
2. You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you miss pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal
birth-control method (such as condoms and/or spermicide) as a backup for those 7 days.
If you MISS 2 white "active" pills in a row in WEEK 1 OR WEEK 2 of your pack:
1. Take 2 pills on the day you remember and 2 pills the next day.
2. Then take 1 pill a day until you finish the pack.
3. You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you miss pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal
birth-control method (such as condoms and/or spermicide) as a backup for those 7 days.
If you MISS 2 white "active" pills in a row in THE 3rd WEEK:
The Day 1 Starter instructions are for the 21-day pill pack only. The 28-day pill pack does not accommodate a
DAY 1 START dosage regimen. The Sunday Starter instructions are for either the 21-day or 28-day pill pack.
1. If you are a Day 1 Starter:
THROW OUT the rest of the pill pack and start a new pack that same day.
If you are a Sunday Starter:
Keep taking 1 pill every day until Sunday.
On Sunday, THROW OUT the rest of the pack and start a new pack of pills that same day.
2. You may not have your period this month but this is expected. However, if you miss your period 2 months in a
row, call your health-care professional because you might be pregnant.
3. You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you miss pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal
birth-control method (such as condoms and/or spermicide) as a backup for those 7 days.
If you MISS 3 OR MORE white "active" pills in a row (during the first 3 weeks):
The Day 1 Starter instructions are for the 21-day pill pack only. The 28-day pill pack does not accommodate a
DAY 1 START dosage regimen. The Sunday Starter instructions are for either the 21-day or 28-day pill pack.
1. If you are a Day 1 Starter:
THROW OUT the rest of the pill pack and start a new pack that same day.
If you are a Sunday Starter:
Keep taking 1 pill every day until Sunday.
On Sunday, THROW OUT the rest of the pack and start a new pack of pills that same day.
2. You may not have your period this month but this is expected. However, if you miss your period 2 months in a
row, call your health-care professional because you might be pregnant.
3. You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you miss pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal
birth-control method (such as condoms and/or spermicide) as a backup for those 7 days.
A REMINDER FOR THOSE ON 28-DAY PACKS
If you forget any of the 7 pink "reminder" pills in Week 4:
THROW AWAY the pills you missed.
Keep taking 1 pill each day until the pack is empty.
You do not need a back-up nonhormonal birth-control method if you start your next pack on time.
FINALLY, IF YOU ARE STILL NOT SURE WHAT TO DO ABOUT THE PILLS YOU HAVE MISSED
Use a BACK-UP NONHORMONAL BIRTH-CONTROL METHOD anytime you have sex.
KEEP TAKING ONE PILL EACH DAY until you can reach your health-care professional.
PREGNANCY DUE TO PILL FAILURE
The incidence of pill failure resulting in pregnancy is approximately 1% if taken every day as directed, but the
average failure rate is approximately 5% including women who do not always take the pill exactly as directed
without missing any pills. If you do become pregnant, the risk to the fetus is minimal, but you should stop
taking your pills and discuss the pregnancy with your health-care professional.
PREGNANCY AFTER STOPPING THE PILL
There may be some delay in becoming pregnant after you stop using oral contraceptives, especially if you had
irregular menstrual cycles before you used oral contraceptives. It may be advisable to postpone conception until
you begin menstruating regularly once you have stopped taking the pill and desire pregnancy.
There does not appear to be any increase in birth defects in newborn babies when pregnancy occurs soon after
stopping the pill.
If you do not desire pregnancy, you should use another method of birth control immediately after stopping the
oral contraceptive pill.
OVERDOSE
Overdosage may cause nausea, vomiting, and fatigue/drowsiness. Withdrawal bleeding may occur in females. In
case of overdosage, contact your health-care professional or pharmacist.
OTHER INFORMATION
Your health-care professional will take a medical and family history before prescribing oral contraceptives
and will examine you. The physical examination may be delayed to another time if you request it and the health-
care professional believes that it is appropriate to postpone it. You should be reexamined at least once a year.
Be sure to inform your health-care professional if there is a family history of any of the conditions listed
previously in this leaflet. Be sure to keep all appointments with your health-care professional, because this
is a time to determine if there are early signs of side effects of oral-contraceptive use.
Do not use the drug for any condition other than the one for which it was prescribed. This drug has been
prescribed specifically for you; do not give it to others who may want birth-control pills.
HEALTH BENEFITS FROM ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
In addition to preventing pregnancy, use of oral contraceptives may provide certain benefits. They are:
� Menstrual cycles may become more regular.
� Blood flow during menstruation may be lighter, and less iron may be lost. Therefore, anemia due to iron
deficiency is less likely to occur.
� Pain or other symptoms during menstruation may be encountered less frequently.
� Ovarian cysts may occur less frequently.
� Ectopic (tubal) pregnancy may occur less frequently.
� Noncancerous cysts or lumps in the breast may occur less frequently.
� Acute pelvic inflammatory disease may occur less frequently.
� Oral-contraceptive use may provide some protection against developing two forms of cancer: cancer of the
ovaries and cancer of the lining of the uterus.
If you want more information about birth-control pills, ask your health-care professional or pharmacist. They
have a more technical leaflet called the Professional Labeling which you may wish to read.
Ovrette Organismes affectes
Les humains et autres mammifères