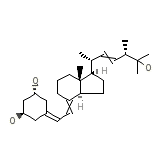
Paricalcitol




Paricalcitol Brand names, Paricalcitol Analogs
Paricalcitol Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
Paricalcitol Chemical_Formula
C27H44O3
Paricalcitol RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic4/zemplar_caps.htm
Paricalcitol fda sheet
Paricalcitol msds (material safety sheet)
Paricalcitol Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
Paricalcitol Molecular Weight
416.636 g/mol
Paricalcitol Melting Point
No information avaliable
Paricalcitol H2O Solubility
No information avaliable
Paricalcitol State
No information avaliable
Paricalcitol LogP
4.031
Paricalcitol Dosage Forms
Solution
Paricalcitol Indication
For treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD) Stage 3 and 4
Paricalcitol Pharmacology
Secondary hyperparathyroidism is characterized by an elevation in parathyroid hormone (PTH) associated with inadequate levels of active vitamin D hormone. The source of vitamin D in the body is from synthesis in the skin and from dietary intake. Vitamin D requires two sequential hydroxylations in the liver and the kidney to bind to and to activate the vitamin D receptor (VDR). The endogenous VDR activator, calcitriol [1,25(OH)2 D3], is a hormone that binds to VDRs that are present in the parathyroid gland, intestine, kidney, and bone to maintain parathyroid function and calcium and phosphorus homeostasis, and to VDRs found in many other tissues, including prostate, endothelium and immune cells. VDR activation is essential for the proper formation and maintenance of normal bone. In the diseased kidney, the activation of vitamin D is diminished, resulting in a rise of PTH, subsequently leading to secondary hyperparathyroidism and disturbances in the calcium and phosphorus homeostasis.1 Decreased levels of 1,25(OH)2 D3 have been observed in early stages of chronic kidney disease. The decreased levels of 1,25(OH)2 D3 and resultant elevated PTH levels, both of which often precede abnormalities in serum calcium and phosphorus, affect bone turnover rate and may result in renal osteodystrophy. An in vitro study indicates that paricalcitol is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 or CYP3A at concentrations up to 50 nM (21 ng/mL).
Paricalcitol Absorption
well absorbed
Paricalcitol side effects and Toxicity
No information avaliable
Paricalcitol Patient Information
No information avaliable
Paricalcitol Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals