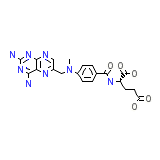
Methotrexate for Injection




Methotrexate for Injection Brand names, Methotrexate for Injection Analogs
- Abitrexate
- Amethopterin
- Amethopterine
- Antifolan
- Arbitrexate
- Emtexate
- Folex
- Folex Pfs
- HDMTX
- L-Amethopterin
- Ledertrexate
- MTX
- Metatrexan
- Methopterin
- Methotextrate
- Methotrate
- Methotrexat
- Methotrexate Lpf
- Methotrexate Preservative Free
- Methotrexate Sodium
- Methotrexate for Injection
- Methotrexate, Usp Grade
- Methylaminopterin
- Methylaminopterinum
- Mexate
- Mexate-Aq
- Mexate-Aq Preserved
- N-Bismethylpteroylglutamic Acid
- Rheumatrex
- Rheumatrex Dose Pack
- Trexall
Methotrexate for Injection Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
Methotrexate for Injection Chemical_Formula
Methotrexate for Injection RX_link
Methotrexate for Injection fda sheet
Methotrexate for Injection msds (material safety sheet)
Methotrexate for Injection Synthesis Reference
Methotrexate for Injection Molecular Weight
Methotrexate for Injection Melting Point
Methotrexate for Injection H2O Solubility
Methotrexate for Injection State
Methotrexate for Injection LogP
Methotrexate for Injection Dosage Forms
Methotrexate for Injection Indication
Methotrexate for Injection Pharmacology
Methotrexate for Injection Absorption
Methotrexate for Injection side effects and Toxicity
Methotrexate for Injection Patient Information
Patients should be informed of the early signs and symptoms of toxicity, of the need to see their physician promptly if they occur, and the need for close follow-up, including periodic laboratory tests to monitor toxicity.
Both the physician and pharmacist should emphasize to the patient that the recommended dose is taken weekly in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis, and that mistaken daily use of the recommended dose has led to fatal toxicity. Patients should be encouraged to read the Patient Instructions sheet within the Dose Pack. Prescriptions should not be written or refilled on a PRN basis.
Patients should be informed of the potential benefit and risk in the use of methotrexate. The risk of effects on reproduction should be discussed with both male and female patients taking methotrexate.