Maninil




Maninil Brand names, Maninil Analogs
- Abbenclamide
- Adiab
- Apo-Glibenclamide
- Azuglucon
- Bastiverit
- Benclamin
- Betanase
- Betanese 5
- Calabren
- Cytagon
- Daonil
- Debtan
- Dia-basan
- Diabeta
- Diabeta (TN)
- Diabiphage
- Dibelet
- Duraglucon
- Euclamin
- Euglucan
- Euglucon
- Euglucon 5
- Euglykon
- GBN 5
- Gen-Glybe
- Gewaglucon
- Gilemal
- Glamide
- Glibadone
- Gliban
- Gliben
- Gliben-Puren N
- Glibenbeta
- Glibenclamid AL
- Glibenclamid Basics
- Glibenclamid Fabra
- Glibenclamid Genericon
- Glibenclamid Heumann
- Glibenclamid Riker M.
- Glibenclamid-Cophar
- Glibenclamid-Ratiopharm
- Glibenclamida [INN-Spanish]
- Glibenclamide
- Glibenclamide (JP14)
- Glibenclamidum [INN-Latin]
- Glibenil
- Glibens
- Glibesyn
- Glibet
- Glibetic
- Glibil
- Gliboral
- Glicem
- Glidiabet
- Glimel
- Glimide
- Glimidstata
- Glisulin
- Glitisol
- Glubate
- Gluben
- Gluco-Tablimen
- Glucobene
- Glucohexal
- Glucolon
- Glucomid
- Glucoremed
- Glucoven
- Glyben
- Glybenclamide
- Glybenzcyclamide
- Glyburide (USP)
- Glyburide (micronized)
- Glyburide [USAN]
- Glycolande
- Glycomin
- Glynase
- Hemi-Daonil
- Hexaglucon
- Humedia
- Lederglib
- Libanil
- Lisaglucon
- Malix
- Maninil
- Med-Glionil
- Melix
- Micronase
- Micronase (TN)
- Miglucan
- Nadib
- Neogluconin
- Norglicem 5
- Normoglucon
- Novo-Glyburide
- Orabetic
- Pira
- Praeciglucon
- PresTab
- Prodiabet
- Renabetic
- Semi-Euglucon
- Semi-Gliben-Puren N
- Semi-daonil
- Sugril
- Suraben
- Tiabet
- Yuglucon
Maninil Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
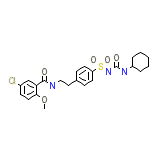
Maninil Chemical_Formula
C23H28ClN3O5S
Maninil RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic/glybur.htm
Maninil fda sheet
Maninil msds (material safety sheet)
Maninil Synthesis Reference
Weber et al., U.S. Pat. 3,454,635 (1969)
Maninil Molecular Weight
494.004 g/mol
Maninil Melting Point
169-170oC
Maninil H2O Solubility
4 mg/L
Maninil State
Solid
Maninil LogP
4.85
Maninil Dosage Forms
Tablet (1.25 mg, 2.5 mg, 5 mg)
Maninil Indication
Indicated as an adjunct to diet to lower the blood glucose in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (Type II) whose hyperglycemia cannot be satisfactorily controlled by diet alone.
Maninil Pharmacology
Glyburide, a second-generation sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent, appears to lower the blood glucose acutely by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas, an effect dependent upon functioning beta cells in the pancreatic islets. With chronic administration in Type II diabetic patients, the blood glucose lowering effect persists despite a gradual decline in the insulin secretory response to the drug. Extrapancreatic effects may be involved in the mechanism of action of oral sulfonyl-urea hypoglycemic drugs. The combination of glyburide and metformin may have a synergistic effect, since both agents act to improve glucose tolerance by different but complementary mechanisms. In addition to its blood glucose lowering actions, glyburide produces a mild diuresis by enhancement of renal free water clearance. Glyburide is twice as potent as the related second-generation agent glipizide.
Maninil Absorption
Significant absorption within 1 hour and peak plasma levels are reached within 4 hours.
Maninil side effects and Toxicity
Oral rat LD50: > 20,000 mg/kg. Oral mouse LD50: 3250 mg/kg.
Maninil Patient Information
Patients should be informed of the potential risks and advantages of MICRONASE and of alternative modes of therapy. They also should be informed about the importance of adherence to dietary instructions, of a regular exercise program, and of regular testing of urine and/or blood glucose.
The risks of hypoglycemia, its symptoms and treatment, and conditions that predispose to its development should be explained to patients and responsible family members. Primary and secondary failure also should be explained.
Maninil Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals