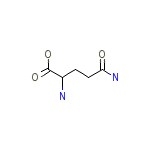
2-Aminoglutaramic acid




2-Aminoglutaramic acid Brand names, 2-Aminoglutaramic acid Analogs
2-Aminoglutaramic acid Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
2-Aminoglutaramic acid Chemical_Formula
C5H10N2O3
2-Aminoglutaramic acid RX_link
No information avaliable
2-Aminoglutaramic acid fda sheet
2-Aminoglutaramic acid msds (material safety sheet)
2-Aminoglutaramic acid Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
2-Aminoglutaramic acid Molecular Weight
146.146 g/mol
2-Aminoglutaramic acid Melting Point
185 oC
2-Aminoglutaramic acid H2O Solubility
Slight (0.1-1%)
2-Aminoglutaramic acid State
Solid
2-Aminoglutaramic acid LogP
-4.102
2-Aminoglutaramic acid Dosage Forms
Capsules, powder, tablets
2-Aminoglutaramic acid Indication
Used for nutritional supplementation, also for treating dietary shortage or imbalance.
2-Aminoglutaramic acid Pharmacology
Like other amino acids, glutamine is biochemically important as a constituent of proteins. Glutamine is also crucial in nitrogen metabolism. Ammonia (formed by nitrogen fixation) is assimilated into organic compounds by converting glutamic acid to glutamine. The enzyme which accomplishes this is called glutamine synthetase. Glutamine can then be used as a nitrogen donor in the biosynthesis of many compounds, including other amino acids, purines, and pyrimidines.
2-Aminoglutaramic acid Absorption
Absorption is efficient and occurs by an active transport mechanism
2-Aminoglutaramic acid side effects and Toxicity
Doses of L-glutamine up to 21 grams daily appear to be well tolerated. Reported adverse reactions are mainly gastrointestinal and not common. They include constipation and bloating. There is one older report of two hypomanic patients whose manic symptoms were exacerbated following the use of 2 to 4 grams daily of L-glutamine. The symptoms resolved when the L-glutamine was stopped. These patients were not rechallenged, nor are there any other reports of this nature.
2-Aminoglutaramic acid Patient Information
No information avaliable
2-Aminoglutaramic acid Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals