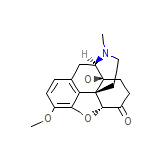
Oxycodone




Categoria
Oxycodone Nombres de marca, Oxycodone Analogos
- Codeinone, Dihydrohydroxy-
- Combunox
- Dea No. 9143
- Dihydrohydroxycodeinone
- Dihydrohydroxycondeinone
- Dihydrone
- Dihydroxycodeinone
- Dinarkon
- Diphydrone
- ENDOCET
- ENDODAN
- Endone
- Eubine
- Eubine [France]
- Eucodal
- Eucodalum
- Eukodal
- Eutagen
- Ossicodone [Dcit]
- Oxanest
- Oxicodona [Inn-Spanish]
- Oxicon
- Oxicone
- Oxikon
- Oxycet
- Oxycodeinone
- Oxycodon
- Oxycodone Hcl
- Oxycodone Hydrochloride
- Oxycodone [Usan:Ban:Inn]
- Oxycodonum [Inn-Latin]
- Oxycon
- Oxycontin
- PERCOCET
- Pancodine
- Percobarb
- Percodan
- Roxicet
- Roxicodone
- Roxilox
- Supendol [Canada]
- Tecodin
- Tekodin
- Thecodine
- Thekodin
- Tylox
Oxycodone Marca los nombres de mezcla
Oxycodone Formula quimica
Oxycodone RX enlace
Oxycodone FDA hoja
Oxycodone MSDS (hoja de seguridad de materiales)
Oxycodone Sintesis de referencia
Oxycodone Peso molecular
Oxycodone Punto de fusion
Oxycodone H2O Solubilidad
Oxycodone Estado
Oxycodone LogP
Oxycodone Formas de dosificacion
Oxycodone Indicacion
Oxycodone Farmacologia
Oxycodone Absorcion
Oxycodone Toxicidad
Oxycodone Informacion de Pacientes
WARNINGS
Drug Dependence: Oxycodone can produce drug dependence of the morphine type, and therefore, has the potential for being abused. Psychic dependence, physical dependence and tolerance may develop upon repeated administration of this drug, and it should be prescribed and administered with the same degree of caution appropriate to the use of other oral narcotic-containing medications. Like other narcotic-containing medications, this drug is subject to the Federal Controlled Substances Act.
Usage in Ambulatory Patients: Oxycodone may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery. The patient using this drug should be cautioned accordingly.
Interaction with Other Central Nervous System Depressants: Patients receiving other narcotic analgesics, general anesthetics, phenothiazines, other tranquilizers, sedative-hypnotics or other CNS depressants (including alcohol) concomitantly with oxycodone hydrochloride may exhibit an additive CNS depression. When such combined therapy is contemplated, the dose of one or both agents should be reduced.
Usage in Pregnancy: Safe use in pregnancy has not been established relative to possible adverse effects on fetal development. Therefore, this drug should not be used in pregnant women unless, in the judgment of the physician, the potential benefits outweigh the possible hazards.
Usage in Children: This drug should not be administered to children.
PRECAUTIONS
Head Injury and Increased Intracranial Pressure: The respiratory depressant effects of narcotics and their capacity to elevate cerebrospinal fluid pressure may be markedly exaggerated in the presence of head injury, other intracranial lesions or a pre-existing increase in intracranial pressure. Furthermore, narcotics produce adverse reactions which may obscure the clinical course of patients with head injuries.
Acute Abdominal Conditions: The administration of this drug or other narcotics may obscure the diagnosis or clinical course in patients with acute abdominal conditions.
Special Risk Patients: This drug should be given with caution to certain patients such as the elderly, or debilitated, and those with severe impairment of hepatic or renal function, hypothyroidism, Addison's disease and prostatic hypertrophy or urethral stricture.