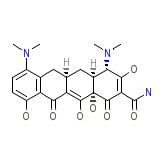
Minocin




Minocin Brand names, Minocin Analogs
Minocin Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
Minocin Chemical_Formula
C23H27N3O7
Minocin RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic/minocycline.htm
Minocin fda sheet
Minocin msds (material safety sheet)
Minocin Synthesis Reference
Boothe, Petisi, U.S. Pat. 3,148,212 (1964)
Minocin Molecular Weight
457.477 g/mol
Minocin Melting Point
No information avaliable
Minocin H2O Solubility
52 mg/mL
Minocin State
Solid
Minocin LogP
0.092
Minocin Dosage Forms
Capsules; Subgingival (sustained-release); IV injection
Minocin Indication
For the treatment of infections caused by susceptible strains of microorganisms, such as Rocky Mountain spotted fever, typhus fever and the typhus group, Q fever, rickettsial pox and tick fevers caused by Rickettsiae, upper respiratory tract infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and for the treatment of asymptomatic carriers of Neisseria meningitidis.
Minocin Pharmacology
Minocycline, the most lipid soluble and most active tetracycline antibiotic, is, like doxycycline, a long-acting tetracycline. Minocycline's effects are related to the inhibition of protein synthesis. Although minocycline's broader spectrum of activity, compared to other members of the group, includes activity against Neisseria meningitidis, its use as a prophylaxis is no longer recomended because of side effects (dizziness and vertigo). Current research is examining the possible neuroprotective effects of minocycline against progression of Huntington's Disease, an inherited neurodegenerative disorder. The neuroprotective action of minocycline may include its inhibitory effect on 5-lipoxygenase, an inflammatory enzyme associated with brain aging.
Minocin Absorption
Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and absorption is not significantly impaired by ingestion of food or milk. Oral bioavailability is 100%.
Minocin side effects and Toxicity
Minocycline has been observed to cause a dark discoloration of the thyroid in experimental animals (rats, minipigs, dogs and monkeys). In the rat, chronic treatment with minocycline has resulted in goiter accompanied by elevated radioactive iodine uptake and evidence of thyroid tumor production. Minocycline has also been found to produce thyroid hyperplasia in rats and dogs. LD50=2380 mg/kg (rat, oral), LD50=3600 mg/kg (mouse, oral)
Minocin Patient Information
Minocin Organisms Affected
Enteric bacteria and other eubacteria