Internolol




Categoria
Internolol Nombres de marca, Internolol Analogos
- Aircrit
- Alinor
- Altol
- Anselol
- Antipressan
- Apo-Atenolol
- Atcardil
- Atecard
- Atehexal
- Atenblock
- Atendol
- Atenet
- Ateni
- Atenil
- Atenol
- Atenol 1A Pharma
- Atenol Acis
- Atenol AL
- Atenol Atid
- Atenol Cophar
- Atenol CT
- Atenol Fecofar
- Atenol Gador
- Atenol Genericon
- Atenol GNR
- Atenol Heumann
- Atenol MSD
- Atenol NM Pharma
- Atenol Nordic
- Atenol PB
- Atenol Quesada
- Atenol Stada
- Atenol Tika
- Atenol Trom
- Atenol Von CT
- Atenol-Mepha
- Atenol-Ratiopharm
- Atenol-Wolff
- Atenolin
- Atenomel
- Atereal
- Aterol
- Betablok
- Betacard
- Betasyn
- Betatop GE
- Blocotenol
- Blokium
- Cardaxen
- Cardiopress
- Corotenol
- Cuxanorm
- Duraatenolol
- Duratenol
- Evitocor
- Farnormin
- Felo-Bits
- Hipres
- Hypoten
- Ibinolo
- Internolol
- Jenatenol
- Juvental
- Lo-Ten
- Loten
- Lotenal
- Myocord
- Normalol
- Normiten
- Noten
- Oraday
- Ormidol
- Panapres
- Plenacor
- Premorine
- Prenolol
- Prenormine
- Prinorm
- Scheinpharm Atenol
- Seles Beta
- Selobloc
- Serten
- Servitenol
- Stermin
- Tenidon
- Teno-Basan
- Tenobloc
- Tenoblock
- Tenolol
- Tenoprin
- Tenoretic
- Tenormin
- Tenormine
- Tensimin
- Tredol
- Unibloc
- Uniloc
- Vascoten
- Vericordin
- Wesipin
- Xaten
Internolol Marca los nombres de mezcla
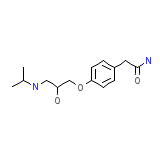
Internolol Formula quimica
C14H22N2O3
Internolol RX enlace
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic/atenolol.htm
Internolol FDA hoja
Internolol MSDS (hoja de seguridad de materiales)
Internolol Sintesis de referencia
Barrett et al., Patente de EE.UU.. 3, 663,607 (1972)
Internolol Peso molecular
266.336 g/mol
Internolol Punto de fusion
146-148oC
Internolol H2O Solubilidad
13,5 mg / ml
Internolol Estado
Solid
Internolol LogP
1.256
Internolol Formas de dosificacion
Tablet (25, 50 y 100 mg), inyección intravenosa
Internolol Indicacion
Para la gestión de hypertention y gestión a largo plazo de los pacientes con angina de pecho
Internolol Farmacologia
Atenolol, un beta competitivos (1)-antagonista selectivo adrenérgico, tiene la más baja solubilidad en lípidos de esta clase de drogas. A pesar de que es similar al metoprolol, atenolol difiere del pindolol y propranolol en el que no tiene propiedades intrínsecas simpaticomiméticos o actividad estabilizadora de membrana. Atenolol se utiliza solo o con clortalidona en el manejo de la hipertensión y el edema.
Internolol Absorcion
dosis por vía oral si rápida y consistencia, pero incompleto. Aproximadamente el 50% de una dosis oral se absorbe en el tracto gastrointestinal, el resto se excreta sin cambios en las heces.
Internolol Toxicidad
LD50 = 2000-3000 mg / kg (por vía oral en ratones). Los síntomas de una sobredosis de atenolol incluyen un latido cardiaco lento, dificultad para respirar, desmayos, mareos, debilidad, confusión, náuseas y vómitos.
Internolol Informacion de Pacientes
This belongs to the group of medicines known as beta-blockers. Atenolol can
be used to treat high blood pressure, angina (chest pain) and irregular
heartbeat. It has varied effects in different parts of the body. High Blood
Pressure: Atenolol works by blocking the transmission of messages to the beta
receptors in the heart which slows down the activity of the heart, decreasing
blood pressure. Angina: Atenolol works by blocking the transmission of messages
to the beta receptors in the heart which slows down the activity of the heart
and reduces the heart's need for oxygen. This makes angina attacks less likely
to occur. Irregular Heartbeat: Normally the heartbeat is regulated by special
tissues which conduct electricity. Some cases of irregular heartbeat are caused
by these tissues conducting electricity too quickly. Atenolol works by reducing
over-activity in the conducting tissue.
be used to treat high blood pressure, angina (chest pain) and irregular
heartbeat. It has varied effects in different parts of the body. High Blood
Pressure: Atenolol works by blocking the transmission of messages to the beta
receptors in the heart which slows down the activity of the heart, decreasing
blood pressure. Angina: Atenolol works by blocking the transmission of messages
to the beta receptors in the heart which slows down the activity of the heart
and reduces the heart's need for oxygen. This makes angina attacks less likely
to occur. Irregular Heartbeat: Normally the heartbeat is regulated by special
tissues which conduct electricity. Some cases of irregular heartbeat are caused
by these tissues conducting electricity too quickly. Atenolol works by reducing
over-activity in the conducting tissue.
Internolol Organismos afectados
Humanos y otros mamíferos