Laraflex




Laraflex Brand names, Laraflex Analogs
Laraflex Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
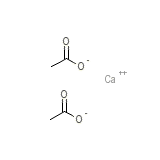
Laraflex Chemical_Formula
C4H6CaO4
Laraflex RX_link
No information avaliable
Laraflex fda sheet
Laraflex msds (material safety sheet)
Laraflex Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
Laraflex Molecular Weight
158.17 g/mol
Laraflex Melting Point
> 160 oC
Laraflex H2O Solubility
No information avaliable
Laraflex State
Solid
Laraflex LogP
No information avaliable
Laraflex Dosage Forms
Capsule; Drops; Liquid; Powder for solution; Solution; Tablet
Laraflex Indication
Used to treat hyperphosphatemia (too much phosphate in the blood) in patients with kidney disease.
Laraflex Pharmacology
Patients with advanced renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min) exhibit phosphate retention and some degree of hyperphosphatemia. The retention of phosphate plays a pivotal role in causing secondary hyperparathyroidism associated with osteodystrophy, and soft-tissue calcification. The mechanism by which phosphate retention leads to hyperparathyroidism is not clearly delineated. Therapeutic efforts directed toward the control of hyperphosphatemia include reduction in the dietary intake of phosphate, inhibition of absorption of phosphate in the intestine with phosphate binders, and removal of phosphate from the body by more efficient methods of dialysis. The rate of removal of phosphate by dietary manipulation or by dialysis is insufficient. Dialysis patients absorb 40% to 80% of dietary phosphorus. Therefore, the fraction of dietary phosphate absorbed from the diet needs to be reduced by using phosphate binders in most renal failure patients on maintenance dialysis. Calcium acetate when taken with meals combines with dietary phosphate to form insoluble calcium phosphate which is excreted in the feces. Maintenance of serum phosphorus below 6.0 mg/dl is generally considered as a clinically acceptable outcome of treatment with phosphate binders. Calcium acetate is highly soluble at neutral pH, making the calcium readily available for binding to phosphate in the proximal small intestine.
Laraflex Absorption
40% is absorbed in the fasting state and approximately 30% is absorbed in the nonfasting state following oral administration.
Laraflex side effects and Toxicity
Oral, rat: LD50 = 4280 mg/kg. Symptoms of overdose include mild hypercalcemia (constipation; loss of appetite; nausea and vomiting), and severe hypercalcemia (confusion; full or partial loss of consciousness; incoherent speech).
Laraflex Patient Information
No information avaliable
Laraflex Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals