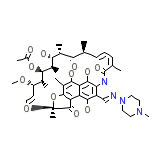
Rifamycin




Rifamycin Brand names, Rifamycin Analogs
Rifamycin Brand Names Mixture
- Rifater (Isoniazid + Pyrazinaamide + Rifampin)
- Rifamate (Rifampin + Isoniazid)
Rifamycin Chemical_Formula
Rifamycin RX_link
Rifamycin fda sheet
Rifamycin msds (material safety sheet)
Rifamycin Synthesis Reference
Rifamycin Molecular Weight
Rifamycin Melting Point
Rifamycin H2O Solubility
Rifamycin State
Rifamycin LogP
Rifamycin Dosage Forms
Rifamycin Indication
Rifamycin Pharmacology
Rifamycin Absorption
Rifamycin side effects and Toxicity
Rifamycin Patient Information
The patient should be told that rifampin may produce a reddish coloration of the urine, sweat, sputum, and tears, and the patient should be forewarned of this. Soft contact lenses may be permanently stained. The patients should be advised that the reliability of oral or other systemic hormonal contraceptives may be affected; consideration should be given to using alternative contraceptive measures. Patients should be instructed to take rifampin either 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal with a full glass of water. Patients should be instructed to notify their physicians promptly if they experience any of the following: fever, loss of appetite, malaise, nausea and vomiting, darkened urine, yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes, and pain or swelling of the joints. Compliance with the full course of therapy must be emphasized, and the importance of not missing any doses must be stressed.