Methodrexitone




Methodrexitone Brand names, Methodrexitone Analogs
Methodrexitone Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
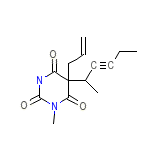
Methodrexitone Chemical_Formula
C14H18N2O3
Methodrexitone RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic3/methohexital.htm
Methodrexitone fda sheet
Methodrexitone msds (material safety sheet)
Methodrexitone Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
Methodrexitone Molecular Weight
262.304 g/mol
Methodrexitone Melting Point
No information avaliable
Methodrexitone H2O Solubility
No information avaliable
Methodrexitone State
Solid
Methodrexitone LogP
1.724
Methodrexitone Dosage Forms
Powder for solution
Methodrexitone Indication
Indicated for use as an intravenous anaesthetic.
Methodrexitone Pharmacology
Methohexital, a barbiturate, is used for the induction of anesthesia prior to the use of other general anesthetic agents and for induction of anesthesia for short surgical, diagnostic, or therapeutic procedures associated with minimal painful stimuli. Little analgesia is conferred by barbiturates; their use in the presence of pain may result in excitation.
Methodrexitone Absorption
The absolute bioavailability following rectal administration of methohexital is 17%.
Methodrexitone side effects and Toxicity
The onset of toxicity following an overdose of intravenously administered methohexital will be within seconds of the infusion. If methohexital is administered rectally or is ingested, the onset of toxicity may be delayed. The manifestations of an ultrashort-acting barbiturate in overdose include central nervous system depression, respiratory depression, hypotension, loss of peripheral vascular resistance, and muscular hyperactivity ranging from twitching to convulsive-like movements. Other findings may include convulsions and allergic reactions. Following massive exposure to any barbiturate, pulmonary edema, circulatory collapse with loss of peripheral vascular tone, and cardiac arrest may occur.
Methodrexitone Patient Information
When appropriate, patients should be instructed as to the hazards of drowsiness that may follow use of barbiturates. Outpatients should be released in the company of another individual, and no skilled activities, such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle, should be engaged in for 8 to 12 hours.
Methodrexitone Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals