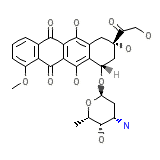
Doxorubicin




Categoria
Doxorubicin Nombres de marca, Doxorubicin Analogos
Doxorubicin Marca los nombres de mezcla
Doxorubicin Formula quimica
Doxorubicin RX enlace
Doxorubicin FDA hoja
Doxorubicin MSDS (hoja de seguridad de materiales)
Doxorubicin Sintesis de referencia
Doxorubicin Peso molecular
Doxorubicin Punto de fusion
Doxorubicin H2O Solubilidad
Doxorubicin Estado
Doxorubicin LogP
Doxorubicin Formas de dosificacion
Doxorubicin Indicacion
Doxorubicin Farmacologia
Doxorubicin Absorcion
Doxorubicin Toxicidad
Doxorubicin Informacion de Pacientes
Patients and their caregivers should be informed of the expected adverse effects of DOXIL® , particularly hand-foot syndrome, stomatitis, and neutropenia and related complications of neutropenic fever, infection, and sepsis.
Hand-Foot Syndrome (HFS): Patients who experience tingling or burning, redness, flaking, bothersome swelling, small blisters, or small sores on the palms of their hands or soles of their feet (symptoms of Hand-Foot Syndrome) should notify their physician.
Stomatitis: Patients who experience painful redness, swelling, or sores in the mouth (symptoms of stomatitis) should notify their physician.
Fever and Neutropenia Patients who develop a fever of 100.5°F or higher should notify their physician.
Nausea, vomiting, tiredness, weakness, rash, or mild hair loss Patients who develop any of these symptoms should notify their physician.
Following its administration, DOXIL® may impart a reddish orange color to the urine and other body fluids. This nontoxic reaction is due to the color of the product and will dissipate as the drug is eliminated from the body.