dl-Tetramisol




dl-Tetramisol Brand names, dl-Tetramisol Analogs
dl-Tetramisol Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
dl-Tetramisol Chemical_Formula
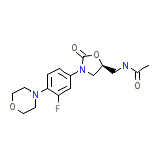
C16H20FN3O4
dl-Tetramisol RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic3/linezolid.htm
dl-Tetramisol fda sheet
dl-Tetramisol msds (material safety sheet)
dl-Tetramisol Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
dl-Tetramisol Molecular Weight
337.346 g/mol
dl-Tetramisol Melting Point
No information avaliable
dl-Tetramisol H2O Solubility
3 mg/mL
dl-Tetramisol State
Solid
dl-Tetramisol LogP
0.232
dl-Tetramisol Dosage Forms
Solution; Tablets
dl-Tetramisol Indication
For the treatment of bacterial infections caused by susceptible strains of vancomycin resistant Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcal aureus (methicillin resistant and susceptible strains), Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae.
dl-Tetramisol Pharmacology
Linezolid is a synthetic antibacterial agent of a new class of antibiotics, the oxazolidinones, which has clinical utility in the treatment of infections caused by aerobic Gram-positive bacteria. The in vitro spectrum of activity of linezolid also includes certain Gram-negative bacteria and anaerobic bacteria. Susceptible organisms include methicillin- and vancomycin-resistant staphylococci, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, penicillin-resistant pneumococci and anaerobes. Oxazolidinones inhibit protein synthesis by binding at the P site at the ribosomal 50S subunit. Resistance to other protein synthesis inhibitors does not affect oxazolidinone activity, however rare development of oxazolidinone resistance cases, associated with 23S rRNA alterations during treatment have been reported. Linezolid inhibits bacterial protein synthesis through a mechanism of action different from that of other antibacterial agents; therefore, cross-resistance between linezolid and other classes of antibiotics is unlikely.
dl-Tetramisol Absorption
Linezolid is rapidly and extensively absorbed after oral dosing. Maximum plasma concentrations are reached approximately 1 to 2 hours after dosing, and the absolute bioavailability is approximately 100%.
dl-Tetramisol side effects and Toxicity
Clinical signs of acute toxicity lead to decreased activity, ataxia, vomiting and tremors.
dl-Tetramisol Patient Information
dl-Tetramisol Organisms Affected
Gram negative and gram positive bacteria