Vigamox




Vigamox Brand names, Vigamox Analogs
Vigamox Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
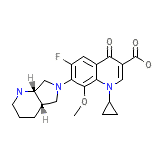
Vigamox Chemical_Formula
C21H24FN3O4
Vigamox RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic3/vigamox.htm
Vigamox fda sheet
Vigamox msds (material safety sheet)
Vigamox Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
Vigamox Molecular Weight
401.431 g/mol
Vigamox Melting Point
238-242 oC
Vigamox H2O Solubility
No information avaliable
Vigamox State
Solid
Vigamox LogP
2.033
Vigamox Dosage Forms
Solution (250 mL bags containing 400 mg of drug); Tablets (400 mg)
Vigamox Indication
For the treatment of sinus and lung infections such as sinusitis, pneumonia, and secondary infections in chronic bronchitis. Also for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis (pinkeye).
Vigamox Pharmacology
Moxifloxacin is a quinolone/fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Moxifloxacin can be used to treat infections caused by the following bacteria: Aerobic Gram-positive microorganisms: Corynebacterium species, Micrococcus luteus, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus hominis, Staphylococcus warneri, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Streptococcus viridans group. Aerobic Gram-negative microorganisms: Acinetobacter lwoffii, Haemophilus influenzae, and Haemophilus parainfluenzae. Other microorganisms: Chlamydia trachomatis.
Moxifloxacin is bactericidal and its mode of action depends on blocking of bacterial DNA replication by binding itself to an enzyme called DNA gyrase, which allows the untwisting required to replicate one DNA double helix into two. Notably the drug has 100 times higher affinity for bacterial DNA gyrase than for mammalian. Moxifloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Moxifloxacin is bactericidal and its mode of action depends on blocking of bacterial DNA replication by binding itself to an enzyme called DNA gyrase, which allows the untwisting required to replicate one DNA double helix into two. Notably the drug has 100 times higher affinity for bacterial DNA gyrase than for mammalian. Moxifloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Vigamox Absorption
Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Absolute oral bioavailability is approximately 90%. Food has little effect on absorption.
Vigamox side effects and Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include CNS and gastrointestinal effects such as decreased activity, somnolence, tremor, convulsions, vomiting, and diarrhea. The minimal lethal intravenous dose in mice and rats is 100 mg/kg.
Vigamox Patient Information
Avoid contaminating the applicator tip with material from the eye, fingers or other source. Systemically administered quinolones including moxifloxacin have been associated with hypersensitivity reactions, even following a single dose. Discontinue use immediately and contact your physician at the first sign of a rash or allergic reaction.
Vigamox Organisms Affected
Enteric bacteria and other eubacteria