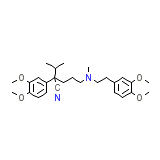
Verapamil




Verapamil Brand names, Verapamil Analogs
- Apo-Verap
- Arpamyl
- Berkatens
- Calan
- Calan SR
- Cardiagutt
- Cardibeltin
- Cordilox
- Covera-HS
- Dignover
- Dilacoran
- Drosteakard
- Geangin
- Iproveratril
- Isoptimo
- Isoptin
- Isoptin SR
- Novo-Veramil
- NU-Verap
- Quasar
- Securon
- Univer
- Vasolan
- Veracim
- Veramex
- Verapamil HCl
- Verapamil [Usan:Ban:Inn]
- Verapamilo [Inn-Spanish]
- Verapamilum [Inn-Latin]
- Veraptin
- Verelan
- Verelan PM
- Verexamil
Verapamil Brand Names Mixture
- Tarka (trandolapril + verapamil hydrochloride)
Verapamil Chemical_Formula
Verapamil RX_link
Verapamil fda sheet
Verapamil msds (material safety sheet)
Verapamil Synthesis Reference
Verapamil Molecular Weight
Verapamil Melting Point
Verapamil H2O Solubility
Verapamil State
Verapamil LogP
Verapamil Dosage Forms
Verapamil Indication
Verapamil Pharmacology
Verapamil Absorption
Verapamil side effects and Toxicity
Verapamil Patient Information
Verapamil HCl is known as a calcium channel blocker. It is taken to treat high blood pressure, to relieve some chest pains in patients with angina, or to treat some problems with heart rhythms. Verapamil has several drug interactions, make sure your physician and pharmacist known all the medicines you are taking so they may properly advise you. Verapamil HCl is excreted in breast milk. It may be necessary to change therapy or provide an alternate to breast milk. The most common side effect is constipation. This may be relieved with dietary modification (more fiber) or laxatives. Sustained release tablets should be taken with food. They should not be broken or crushed. Doses may need some adjustment, make sure to have your condition monitored regularly.