Solgol




Solgol Brand names, Solgol Analogs
Solgol Brand Names Mixture
- Corzide Tab W Nadolol 40mg (Bendroflumethiazide + Nadolol)
- Corzide Tab W Nadolol 80mg (Bendroflumethiazide + Nadolol)
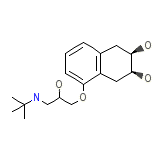
Solgol Chemical_Formula
C17H27NO4
Solgol RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic3/nadolol.htm
Solgol fda sheet
Solgol msds (material safety sheet)
Solgol Synthesis Reference
F. P. Hauck et al., U.S. Pat. 3,935,267 (1976)
Solgol Molecular Weight
309.401 g/mol
Solgol Melting Point
124-136 oC
Solgol H2O Solubility
8330 mg/L
Solgol State
Solid
Solgol LogP
1.398
Solgol Dosage Forms
Tablets (20 mg, 40 mg, 80 mg, 120 mg, and 160 mg)
Solgol Indication
Used in cardiovascular disease to treat arrhythmias, angina pectoris, and hypertension.
Solgol Pharmacology
Nadolol is a nonselective beta-adrenergic receptor antagonist with a long half-life, and is structurally similar to propranolol. Clinical pharmacology studies have demonstrated beta-blocking activity by showing (1) reduction in heart rate and cardiac output at rest and on exercise, (2) reduction of systolic and diastolic blood pressure at rest and on exercise, (3) inhibition of isoproterenol-induced tachycardia, and (4) reduction of reflex orthostatic tachycardia. Nadolol has no intrinsic sympathomimetic activity and, unlike some other beta-adrenergic blocking agents, nadolol has little direct myocardial depressant activity and does not have an anesthetic-like membrane-stabilizing action.
Solgol Absorption
Absorption of nadolol after oral dosing is variable, averaging about 30 percent.
Solgol side effects and Toxicity
Oral, mouse: LD50 = 4500mg/kg. Symptoms of overdose include abdominal irritation, central nervous system depression, coma, extremely slow heartbeat, heart failure, lethargy, low blood pressure, and wheezing.
Solgol Patient Information
Patients, especially those with evidence of coronary artery insufficiency, should be warned against interruption or discontinuation of nadolol therapy without the physician's advice. Although cardiac failure rarely occurs in properly selected patients, patients being treated with beta-adrenergic blocking agents should be advised to consult the physician at the first sign or symptom of impending failure. The patient should also be advised of a proper course in the event of an inadvertently missed dose.
Solgol Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals