Reomax




Reomax Brand names, Reomax Analogs
Reomax Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
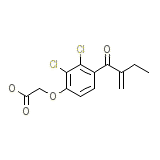
Reomax Chemical_Formula
C13H12Cl2O4
Reomax RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic3/edecrin.htm
Reomax fda sheet
Reomax msds (material safety sheet)
Reomax Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
Reomax Molecular Weight
303.137 g/mol
Reomax Melting Point
122.5 oC
Reomax H2O Solubility
No information avaliable
Reomax State
Solid
Reomax LogP
3.414
Reomax Dosage Forms
Tablet (25, 50 mg); Powder for solution
Reomax Indication
For the treatment of high blood pressure and edema caused by diseases like congestive heart failure, liver failure, and kidney failure.
Reomax Pharmacology
Ethacrynic acid is a monosulfonamyl loop or high ceiling diuretic. Ethacrynic acid acts on the ascending limb of the loop of Henle and on the proximal and distal tubules. Urinary output is usually dose dependent and related to the magnitude of fluid accumulation. Water and electrolyte excretion may be increased several times over that observed with thiazide diuretics, since ethacrynic acid inhibits reabsorption of a much greater proportion of filtered sodium than most other diuretic agents. Therefore, ethacrynic acid is effective in many patients who have significant degrees of renal insufficiency. Ethacrynic acid has little or no effect on glomerular filtration or on renal blood flow, except following pronounced reductions in plasma volume when associated with rapid diuresis.
Reomax Absorption
Onset of action is rapid, usually within 30 minutes after an oral dose of ethacrynic acid or within 5 minutes after an intravenous injection of ethacrynic acid.
Reomax side effects and Toxicity
Overdosage may lead to excessive diuresis with electrolyte depletion.
Reomax Patient Information
No information avaliable
Reomax Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals