Reno-dip




Reno-dip Brand names, Reno-dip Analogs
- Acide amidotrizoique
- Acidum amidotrizoicum
- Acidum diacetylaminotrijodbenzoicum
- AmiDOTrizoic acid
- Amidotrizoate
- Angiovist 282
- Cardiografin
- Conray 35
- DIAT [German]
- Diat
- Diatriazoate
- Diatrizoate sodium
- Diatrizoate sodium salt
- Diatrizoesaeure
- Diatrizoesaure
- Diatrizoesaure [German]
- Diatrizoic acid
- Diatrizoic acid [USAN:BAN]
- Diatrizoic acid sodium salt
- Gastrografin
- Hypaque
- Hypaque 50
- Hypaque sodium
- Iothalamate
- Meglumine diatrizoate
- Methalamic acid
- Odiston
- Reno-dip
- Renografin 76
- Sodium amidotrizoate
- Sodium diatrizoate
- Triombrin
- Triombrin [Russian]
- Triombrine
- Urografic acid, sodium salt
- Urografin acid
- Urogranoic acid
- Urotrast
- Urovison
- Urovist Cysto
- Urovist Cysto Pediatric
- Urovist Meglumine Diu/ct
- Urovist Sodium 300
- Vascoray
Reno-dip Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
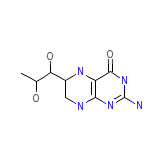
Reno-dip Chemical_Formula
C9H15N5O3
Reno-dip RX_link
No information avaliable
Reno-dip fda sheet
Reno-dip msds (material safety sheet)
Reno-dip Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
Reno-dip Molecular Weight
241.247 g/mol
Reno-dip Melting Point
250-255 oC (hydrochloride salt)
Reno-dip H2O Solubility
>20 mg/mL (dichloride salt)
Reno-dip State
Solid
Reno-dip LogP
-1.783
Reno-dip Dosage Forms
No information avaliable
Reno-dip Indication
For the treatment of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) deficiency.
Reno-dip Pharmacology
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) is used to convert several amino acids, including phenylalanine, to other essential molecules in the body including neurotransmitters. Tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency can be caused by mutations in GTP cyclohydrolase 1 (GCH1), 6-pyruvoyl-tetrahydropterin synthase/dimerization cofactor of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha (PCBD1), 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase (PTS), and quinoid dihydropteridine reductase (QDPR) genes. These genes make the enzymes that are critical for producing and recycling tetrahydrobiopterin. If one of the enzymes fails to function correctly because of a gene mutation, little or no tetrahydrobiopterin is produced. As a result, phenylalanine from the diet builds up in the bloodstream and other tissues and can damage nerve cells in the brain. High levels of phenylalanine can result in signs and symptoms ranging from temporary low muscle tone to mental retardation, movement disorders, difficulty swallowing, seizures, behavioral problems, progressive problems with development, and an inability to control body temperature.
Reno-dip Absorption
No information avaliable
Reno-dip side effects and Toxicity
No information avaliable
Reno-dip Patient Information
No information avaliable
Reno-dip Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals