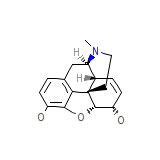
Morphia




Morphia Brand names, Morphia Analogs
- (-)-Heroin hydrochloride
- (-)-Morphine
- Apokyn
- Astramorph PF
- Avinza
- D-(-)-Morphine
- Depodur
- Diacetylmorphine hydrochloride
- Diamorphine hydrochloride
- Dulcontin
- Duramorph PF
- Duromorph
- Epimorph
- Heroin hydrochloride
- Heroine hydrochloride
- Kadian
- M-Eslon
- M.O.S
- MS/L
- MS/S
- MSIR
- Meconium
- Morfina
- Morphia
- Morphin
- Morphina
- Morphine Extra-Forte
- Morphine Forte
- Morphine H.P
- Morphine Sulfate
- Morphinism
- Morphinum
- Morphitec
- Morphium
- Moscontin
- Ms Contin
- Nepenthe
- O,O'-Diacetylmorphine hydrochloride
- OMS Concentrate
- Oramorph SR
- Ospalivina
- RMS Uniserts
- Rescudose
- Roxanol
- Roxanol 100
- Roxanol UD
- Statex
- Statex Drops
- l-Morphine
Morphia Brand Names Mixture
- Camphorated Opium Tincture (Benzoic Acid + Camphor + Morphine)
- Paregorique (Camphor + Morphine)
Morphia Chemical_Formula
Morphia RX_link
Morphia fda sheet
Morphia msds (material safety sheet)
Morphia Synthesis Reference
Morphia Molecular Weight
Morphia Melting Point
Morphia H2O Solubility
Morphia State
Morphia LogP
Morphia Dosage Forms
Morphia Indication
Morphia Pharmacology
Morphia Absorption
Morphia side effects and Toxicity
Morphia Patient Information
If clinically advisable, patients receiving ORAMORPH SR brand of morphine sulfate sustained release tablets, should be given the following instructions by the physician:
- Morphine may produce psychological and/or physical dependence. For this reason, the dose of the drug should not be increased without consulting a physician.
- Morphine may impair mental and/or physical ability required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks (e.g., driving, operating machinery).
- Morphine should not be taken with alcohol or other CNS de-pressants (sleep aids, tranquilizers) because additive effects, including CNS depression, may occur. A physician should be consulted if other prescription and/or over-the-counter medications are currently being used or are prescribed for future use.
- For women of childbearing potential, who become or are planning to become pregnant, a physician should be consulted regarding analgesics and other drug use.
Storage: ORAMORPH SR Tablets should be stored in unopened containers at or below room temperature.
Caution: Federal law prohibits dispensing without prescription. Federal law prohibits the transfer of this drug to any person other than the patient for whom it was prescribed.
Safety and Handling Instructions: ORAMORPH SR is supplied as tablets that pose little risk of direct exposure to health care personnel and should be handled and disposed of in accordance with hospital policy. Patients and their families should be instructed to dispose of ORAMORPH SR tablets, that are no longer needed, down the toilet.