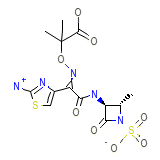
Monobactam




Monobactam Brand names, Monobactam Analogs
Monobactam Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
Monobactam Chemical_Formula
C13H17N5O8S2
Monobactam RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic4/azactaminj.htm
Monobactam fda sheet
Monobactam msds (material safety sheet)
Monobactam Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
Monobactam Molecular Weight
435.435 g/mol
Monobactam Melting Point
No information avaliable
Monobactam H2O Solubility
Insoluble
Monobactam State
Solid
Monobactam LogP
No information avaliable
Monobactam Dosage Forms
Solution (plastic container containing a frozen, iso-osmotic, sterile, sodium-free, nonpyrogenic intravenous solution where each 50 mL of solution contains 1 g, or 2 g aztreonam)
Monobactam Indication
For the treatment of the following infections caused by susceptible gram-negative microorganisms: urinary tract infections, lower respiratory tract infections, septicemia, skin and skin-structure infections, intra-abdominal infections, and gynecologic infections.
Monobactam Pharmacology
Aztreonam is a monocyclic beta-lactam antibiotic (a monobactam) originally isolated from Chromobacterium violaceum. Aztreonam exhibits potent and specific activity in vitro against a wide spectrum of gram-negative aerobic pathogens including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It has no useful activity against gram-positive bacteria or anaerobes, but has very broad spectrum against gram-negative aerobes, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This has given it the nickname "the magic bullet for aerobic gram-negative bacteria". Aztreonam, unlike the majority of beta-lactam antibiotics, does not induce beta-lactamase activity and its molecular structure confers a high degree of resistance to hydrolysis by beta-lactamases (such as penicillinases and cephalosporinases) produced by most gram-negative and gram-positive pathogens; it is, therefore, usually active against gram-negative aerobic microorganisms that are resistant to antibiotics hydrolyzed by beta-lactamases. It is active against many strains that are multiply-resistant to other antibiotics, such as certain cephalosporins, penicillin, and aminoglycosides. Aztreonam maintains its antimicrobial activity over a pH range of 6 to 8 in vitro, as well as in the presence of human serum and under anaerobic conditions.
Monobactam Absorption
Less than 1% absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration. Completely absorbed following intramuscular administration.
Monobactam side effects and Toxicity
No information avaliable
Monobactam Patient Information
No information avaliable
Monobactam Organisms Affected
Enteric bacteria and other eubacteria