Efrane




Efrane Brand names, Efrane Analogs
Efrane Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
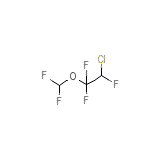
Efrane Chemical_Formula
C3H2ClF5O
Efrane RX_link
No information avaliable
Efrane fda sheet
Efrane msds (material safety sheet)
Efrane Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
Efrane Molecular Weight
184.492 g/mol
Efrane Melting Point
56 oC (boiling point)
Efrane H2O Solubility
Practically insoluble (5620 mg/L)
Efrane State
Liquid
Efrane LogP
2.597
Efrane Dosage Forms
Liquid
Efrane Indication
Used for the induction and maintenance of general anaesthesia during surgery and cesarean section and also used for analgesia during vaginal delivery.
Efrane Pharmacology
Enflurane is an extremely stable halogenated ether inhalation anesthetic that allows rapid adjustments of anesthesia depth with little change in pulse or respiratory rate. Enflurane induces muscle relaxation and reduces pains sensitivity by altering tissue excitability. Induction of and recovery from anesthesia with enflurane are rapid. Enflurane may provide a mild stimulus to salivation or tracheobronchial secretions. Pharyngeal and laryngeal reflexes are readily obtunded. In the cardiovascular system, enflurane is a mild negative inotrope, causing a marked decrease in systemic vascular resistance, thus leading to a decrease in mean arterial pressure. This results in a reflex tachycardia. Enflurane also decreases coronary vascular resistance and sensitizes the myocardium to circulating catecholamines. Enflurane is a strong respiratory depressant. It decreases tidal volume but may increase respiratory rate. It also causes bronchodilatationa and inhibits pulmonary macrophage activity and mucociliary activity. Enflurane principle action in the CNS is general anaesthesia with little analgesic effect. It causes increased cerebral blood flow in concentrations and may induce tonic/clonic muscle activity and epileptiform EEG traces. It also causes a marked decrease in skeletal muscle tone. Actions in the genitourinary system include a decreased renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate and the tone of pregnant uterus is decreased.
Efrane Absorption
Rapidly absorbed into the circulation via the lungs.
Efrane side effects and Toxicity
LD50=5.4 ml/kg (oral, rat). Symptoms of acute overdose include nausea, vomiting, irritation to the eyes, skin and nose/throat, headache, dizziness, and drowsiness. Symptoms of chronic overdose include hypotension, cardiac arrhythmias, respiratory depression, and liver/kidney dysfunction.
Efrane Patient Information
No information avaliable
Efrane Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals