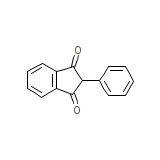
Bindan




Bindan Brand names, Bindan Analogs
- Athrombon
- Bindan
- Cronodione
- Danedion
- Danilon
- Danilone
- Diadilan
- Dindevan
- Dineval
- Diophindane
- Emandion
- Emandione
- Eridione
- Fenhydren
- Fenilin
- Fenindion
- Hedulin
- Hemolidione
- Indema
- Indion
- Indon
- PID
- Phenhydren
- Phenillin
- Phenylen
- Phenylin
- Phenylindanedione
- Phenylindione
- Phenyline
- Phenyllin
- Pindione
- Rectadione
- Theradione
- Thrombasal
- Tromazal
- Trombol
Bindan Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
Bindan Chemical_Formula
C15H10O2
Bindan RX_link
No information avaliable
Bindan fda sheet
Bindan msds (material safety sheet)
Bindan Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
Bindan Molecular Weight
222.239 g/mol
Bindan Melting Point
148-151 oC
Bindan H2O Solubility
27 mg/L (at 20 oC)
Bindan State
Solid
Bindan LogP
2.917
Bindan Dosage Forms
Tablet
Bindan Indication
For the treatment of pulmonary embolism, cardiomyopathy, atrial fibrillation and flutter, cerebral embolism, mural thrombosis, and thrombophili. Also used for anticoagulant prophylaxis.
Bindan Pharmacology
Phenindione thins the blood by antagonizing vitamin K which is required for the production of clotting factors in the liver. Anticoagulants such as Phenindione have no direct effect on an established thrombus, nor do they reverse ischemic tissue damage (damage caused by an inadequate blood supply to an organ or part of the body). However, once a thrombus has occurred, the goal of anticoagulant treatment is to prevent further extension of the formed clot and prevent secondary thromboembolic complications which may result in serious and possibly fatal sequelae. Phenindione has actions similar to warfarin, but it is now rarely employed because of its higer incidence of severe adverse effects.
Bindan Absorption
Absorbed slowly from the gastrointestinal tract.
Bindan side effects and Toxicity
Oral, mouse: LD50 = 175 mg/kg; Oral, rat: LD50 = 163 mg/kg.
Bindan Patient Information
No information avaliable
Bindan Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals