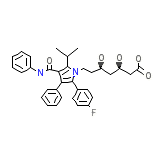
Atorvastatin calcium




Atorvastatin calcium Brand names, Atorvastatin calcium Analogs
Atorvastatin calcium Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
Atorvastatin calcium Chemical_Formula
C33H35FN2O5
Atorvastatin calcium RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic/atorvastatin.htm
Atorvastatin calcium fda sheet
Atorvastatin calcium msds (material safety sheet)
Atorvastatin calcium Synthesis Reference
B.D. Roth, U.S. pat. 5,273, 995(1991, 1993)
Atorvastatin calcium Molecular Weight
558.64 g/mol
Atorvastatin calcium Melting Point
159.2-160.7oC
Atorvastatin calcium H2O Solubility
Sodium salt soluble in water, 20.4 ug/mL (pH 2.1), 1.23 mg/mL (pH 6.0)
Atorvastatin calcium State
Solid
Atorvastatin calcium LogP
6.259
Atorvastatin calcium Dosage Forms
Tablet (10 mg, 20 mg, or 40 mg)
Atorvastatin calcium Indication
For management as an adjunct to diet to reduce elevated total-C, LDL-C, apo B, and TG levels in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia.
Atorvastatin calcium Pharmacology
Atorvastatin, a selective, competitive HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, is used to lower cholesterol and triglycerides in patients with hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia and in the treatment of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Atorvastatin has a unique structure, long half-life, and hepatic selectivity, explaining its greater LDL-lowering potency compared to other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors.
Atorvastatin calcium Absorption
Atorvastatin is rapidly absorbed after oral administration. The absolute bioavailability of atorvastatin (parent drug) is approximately 14% and the systemic availability of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activity is approximately 30%.
Atorvastatin calcium side effects and Toxicity
Rhabdomyolysis, eye hemorrhages, and liver problems.
Atorvastatin calcium Patient Information
Lipitor is a HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor, also known as a statin. This class
of treatments for high cholesterol is fairly new, and appears to work by
blocking a liver enzyme which generates cholesterol. This medication appears
to be the most effective in this class of drugs at lowering unhealthy LDL
(low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels, in some cases up to 51%. It
can be virtually as effective as an angioplasty in treating stable coronary
artery disease. Currently, this drug is approved for use in patients with
high cholesterol (hypercholesterolemia) due to high LDL levels, hereditary
elevated fat levels (dysbetalipoproteinemia), familial high cholesterol,
and to increase HDL (high-density lipoprotein) levels in patients with high
cholesterol and those with both high cholesterol and high triglycerides (mixed
dyslipidemia). Other accepted uses include the treatment of stable coronary
artery diseas, preventing coronary heart disease, preventing clogged stents
(tubes) placed in coronary arteries after surgery, preventing bone loss in
type two diabetics, stabilizing lipid levels that have been altered by treatment
with protease inhibitors. This treatment should be considered a last resort.
The best way to lower cholesterol is through a program of healthy diet and
exercise, and these should be maintained during treatment with Lipitor.
of treatments for high cholesterol is fairly new, and appears to work by
blocking a liver enzyme which generates cholesterol. This medication appears
to be the most effective in this class of drugs at lowering unhealthy LDL
(low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels, in some cases up to 51%. It
can be virtually as effective as an angioplasty in treating stable coronary
artery disease. Currently, this drug is approved for use in patients with
high cholesterol (hypercholesterolemia) due to high LDL levels, hereditary
elevated fat levels (dysbetalipoproteinemia), familial high cholesterol,
and to increase HDL (high-density lipoprotein) levels in patients with high
cholesterol and those with both high cholesterol and high triglycerides (mixed
dyslipidemia). Other accepted uses include the treatment of stable coronary
artery diseas, preventing coronary heart disease, preventing clogged stents
(tubes) placed in coronary arteries after surgery, preventing bone loss in
type two diabetics, stabilizing lipid levels that have been altered by treatment
with protease inhibitors. This treatment should be considered a last resort.
The best way to lower cholesterol is through a program of healthy diet and
exercise, and these should be maintained during treatment with Lipitor.
Atorvastatin calcium Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals