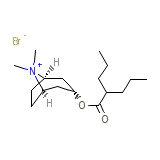
Anisotropine methobromide




Anisotropine methobromide Brand names, Anisotropine methobromide Analogs
Anisotropine methobromide Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
Anisotropine methobromide Chemical_Formula
C17H32BrNO2
Anisotropine methobromide RX_link
No information avaliable
Anisotropine methobromide fda sheet
Anisotropine methobromide msds (material safety sheet)
Anisotropine methobromide Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
Anisotropine methobromide Molecular Weight
362.346 g/mol
Anisotropine methobromide Melting Point
329 oC
Anisotropine methobromide H2O Solubility
1600 mg/L
Anisotropine methobromide State
Solid
Anisotropine methobromide LogP
0.60
Anisotropine methobromide Dosage Forms
Tablet (oral, 50mg)
Anisotropine methobromide Indication
For use in conjunction with antacids or histamine H2-receptor antagonists in the treatment of peptic ulcer, to reduce further gastric acid secretion and delay gastric emptying.
Anisotropine methobromide Pharmacology
Anisotropine methylbromide is a quaternary ammonium compound. Its use as treatment adjunct in peptic ulcer has been replaced by the use of more effective agents. Depending on the dose, anisotropine methylbromide may reduce the motility and secretory activity of the gastrointestinal system, and the tone of the ureter and urinary bladder and may have a slight relaxant action on the bile ducts and gallbladder. In general, smaller doses of anisotropine methylbromide inhibit salivary and bronchial secretions, sweating, and accommodation; cause dilatation of the pupil; and increase the heart rate. Larger doses are required to decrease motility of the gastrointestinal and urinary tracts and to inhibit gastric acid secretion.
Anisotropine methobromide Absorption
Gastrointestinal absorption is poor and irregular. Total absorption after an oral dose is about 10 to 25%.
Anisotropine methobromide side effects and Toxicity
No information avaliable
Anisotropine methobromide Patient Information
Anisotropine methobromide Organisms Affected
Humans and other mammals