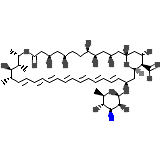
ABLC




ABLC Brand names, ABLC Analogs
ABLC Brand Names Mixture
- No information avaliable
ABLC Chemical_Formula
C47H73NO17
ABLC RX_link
http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic2/amphoter.htm
ABLC fda sheet
ABLC msds (material safety sheet)
ABLC Synthesis Reference
No information avaliable
ABLC Molecular Weight
924.079 g/mol
ABLC Melting Point
170.0 oC
ABLC H2O Solubility
750 mg/L
ABLC State
Solid
ABLC LogP
0.947
ABLC Dosage Forms
Slow intravenous-infusion
ABLC Indication
Used to treat potentially life threatening fungal infections.
ABLC Pharmacology
Amphotericin B shows a high order of in vitro activity against many species of fungi. Histoplasma capsulatum, Coccidioides immitis, Candida species, Blastomyces dermatitidis, Rhodotorula, Cryptococcus neoformans, Sporothrix schenckii, Mucor mucedo, and Aspergillus fumigatus are all inhibited by concentrations of amphotericin B ranging from 0.03 to 1.0 mcg/mL in vitro. While Candida albicans is generally quite susceptible to amphotericin B, non-albicans species may be less susceptible. Pseudallescheria boydii and Fusarium sp. are often resistant to amphotericin B. The antibiotic is without effect on bacteria, rickettsiae, and viruses.
ABLC Absorption
Bioavailability is 100% for intravenous infusion.
ABLC side effects and Toxicity
Oral, rat: LD50 = >5 gm/kg. Amphotericin B overdoses can result in cardio-respiratory arrest.
ABLC Patient Information
No information avaliable
ABLC Organisms Affected
Various Fungus Species